Common measurement methods for static contact angle
1. Seat drop method
Early static contact angle measurement methods used protractors to determine the baseline with the naked eye. With the development of digital technology, image based contact angle measurement methods emerged. The seat drop method is the simplest, most direct, and less hardware required measurement method, and it is the most widely used. The calculation methods for the contact angle of the droplet method can be divided into non model based and model based methods. Non model based methods do not fully utilize the contour information of the liquid, such as tangent method and width height method; The model-based calculation method requires assuming a contour model in advance, such as a circle, ellipse, or ADSA-P, and then incorporating the liquid contour point set collected from the image into the model to solve the parameters. The theoretical accuracy is greater than the former in the absence of noise interference. The subsequent research mainly focuses on the model of the seat drop method.
2. Inclined plate method
The inclined plate method is generally used for filiform small materials. The material is made into a sample several centimeters long and inserted into the liquid. The included angle between the sample and the liquid surface is adjusted so that the liquid surface at one end of the sample is horizontal. At this time, the included angle between the liquid surface and the sample θ For the contact angle, as shown in Figure 1-2.
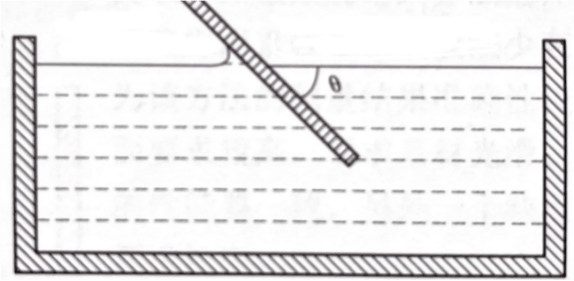
Figure 1-2 Model of inclined plate method
3. Insert board method
The insertion method requires the sample to be vertically inserted into the liquid surface. Assuming that the solid can be wetted by the liquid and reaches equilibrium, the liquid climb height is, and the solid immersion depth is. Therefore, the relationship between them and the contact angle satisfies equations (1-4).
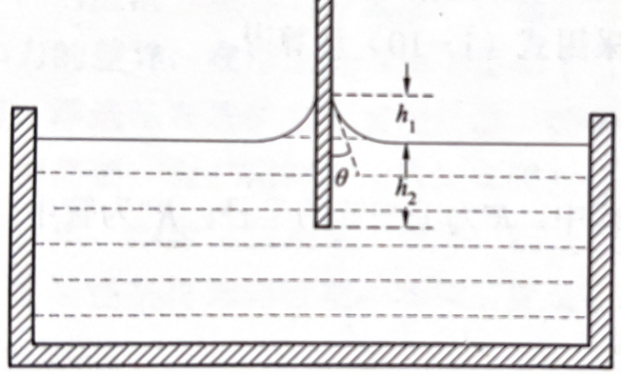
Figure 1-3 Insertion board method
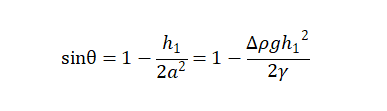
(1-4)
In the formula: represents the interfacial tension between liquid and gas; Represents the acceleration of gravity; The density difference between the liquid and gas phases is represented by the capillary length of the liquid, which is called the capillary constant of the liquid.
When the insertion method is in equilibrium, based on the gravity of the board, the buoyancy of the liquid on the board, surface tension, and the tension of the instrument on the board body, equations 1-5 are satisfied:
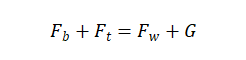
(1-5)
In the formula: obtained through mechanical sensors
For and with:
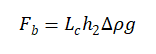
(1-6)

(1-7)
In the formula, is the length of the three-phase contact wire, which is the circumference of the intersection between the plate and the liquid, and is the depth at which the plate is inserted into the liquid. Substitute equations (1-6) and (1-7) into equations (1-5) to obtain
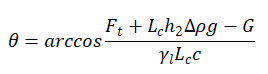
(1-8)
The use of the insertion rule does not require analysis based on the contour of the liquid, but for the test sample, it is necessary to ensure that the surface is sufficiently smooth and that the surface properties are the same everywhere.
4. Bubble trapping method
The bubble trapping method and the seat drop method have a mirror image relationship with each other, as shown in Figures 1-4. For materials with relatively smooth surfaces, their measurement results have been verified by the seat drop method [1]. This method can solve the problem of difficult observation of the profile when the material is relatively hydrophilic, and is useful for controlling the temperature of the testing liquid. The disadvantage is that materials soaked in liquids can easily cause changes in their wetting properties, and testing requires a large amount of liquid, which can easily lead to waste.
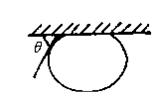
Figure 1-4 Bubble capture method model
PREV:The application of contact angle measuring instrument in contact lenses
NEXT:Application of contact angle meter in wettability analysis of carbon materials

